Although turbine and impeller are sometimes used interchangeably in everyday contexts, in technical and industrial applications their meanings and uses are clearly distinct. A turbine usually refers to a fan in a car or airplane engine that improves engine performance by using exhaust gases to blow fuel vapor into the engine. The impeller is composed of a disc, a wheel cover, a blade and other parts. The fluid rotates with the impeller at high speed under the action of the impeller blades. The gas is affected by the centrifugal force of the rotation and the expansion flow in the impeller, allowing it to pass through the impeller. The pressure behind the impeller is increased.
1. Definition and characteristics of turbine
A turbine is a rotating power machine that converts the energy of a flowing working medium into mechanical work. It is one of the main components of aircraft engines, gas turbines and steam turbines. Turbine blades are usually made of metal or ceramic materials and are used to convert the kinetic energy of fluids into mechanical energy. The design and working principle of turbine blades determine their application in different industrial fields, such as aviation, automobiles, shipbuilding, engineering machinery, etc.

Turbine blades usually consist of three main parts: the inlet section, the intermediate section and the outlet section. The inlet section blades are wider to guide the fluid to the center of the turbine, the middle section blades are thinner to improve turbine efficiency, and the outlet section blades are used to push the remaining fluid out of the turbine. A turbocharger can greatly increase the power and torque of an engine. Generally speaking, the power and torque of an engine after adding a turbocharger will increase by 20% to 30%. However, turbocharging also has its disadvantages, such as turbo lag, increased noise, and exhaust heat dissipation issues.
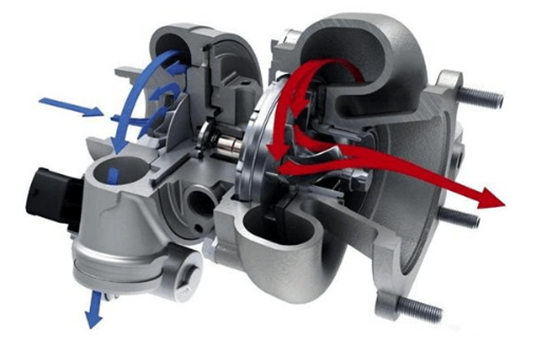
2. Definition and characteristics of impeller
Impeller refers to the wheel disk equipped with moving blades, which is a component of the impulse steam turbine rotor. It can also refer to the general name of the wheel disk and the rotating blades installed on it. Impellers are classified according to their shape and opening and closing conditions, such as closed impellers, semi-open impellers and open impellers. The design and material selection of the impeller depends on the type of fluid it needs to handle and the task it needs to complete.

The main function of the impeller is to convert the mechanical energy of the prime mover into the static pressure energy and dynamic pressure energy of the working fluid. The impeller design must be able to handle and effectively transport liquids containing large particle impurities or long fibers, and must have good anti-clogging performance and efficient operating characteristics. The material selection of the impeller is also very important. Appropriate materials need to be selected according to the nature of the working medium, such as cast iron, stainless steel, bronze and non-metallic materials.
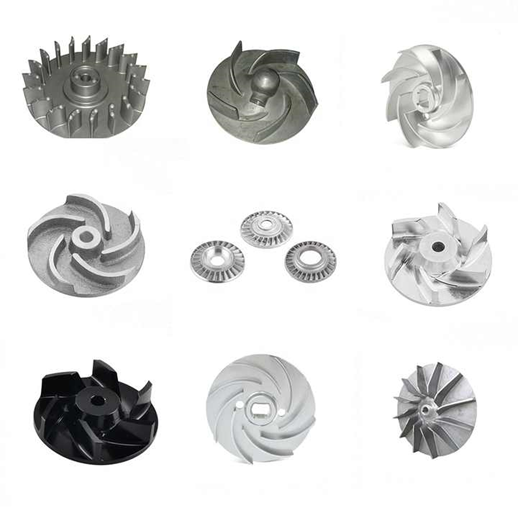

3. Comparison between turbine and impeller
Although turbines and impellers both involve converting fluid kinetic energy into mechanical energy, they have significant differences in their working principles, designs, and applications. A turbine is generally considered an energy extractor in a car or aircraft engine that increases the efficiency of fuel vapor through the exhaust gases, thereby increasing engine performance. The impeller is an energizer that converts mechanical energy into kinetic energy of the fluid through rotation, increases the fluid pressure, and plays a role in various industrial applications, such as pumping liquids containing solid particles.
In turbines, the blades are usually thinner to provide a larger blade area and produce a stronger power output. In an impeller, the blades are usually thicker to provide better resistance and expansion. In addition, turbine blades are usually designed to rotate and directly output power, while impeller blades can be stationary or rotating, depending on the application requirements2.
4、Conclusion
To sum up, there are obvious differences in the definition, characteristics and applications of turbines and impellers. Turbines are primarily used to improve the performance of internal combustion engines, while impellers are used to transport and process fluids in a wide range of industrial applications. The design of the turbine focuses on the extra power and efficiency it can provide, while the impeller emphasizes its reliability and ability to handle a variety of fluids.
Post time: Jun-06-2024





