一、Five important details that are easily overlooked in lost foam casting
1. Pressure head height;
1) In order to ensure the highest and farthest part of the casting, and obtain a casting with clear contours and complete structure, the height from the highest point of the casting to the liquid surface of the pouring cup should meet: hM≥Ltanα
Where: hM--minimum residual pressure head height (mm)
L--the flow of molten metal, the horizontal distance of the center line of the straight runner at the farthest point of the casting (mm)
α--pressure pouring (°)
Sufficient pressure head height, when the molten metal in the cavity rises, there is enough pressure to ensure the filling speed of the molten metal.
2) The foam pattern is vaporized during the pouring process, generating a large amount of gas. On the one hand, the gas is sucked away by the negative pressure, and secondly, it is squeezed out of the cavity by the rising molten metal with sufficient pressure.
3) Defects such as cold shut, pores, and carbon deposition generated on the upper part of the casting are generally caused by insufficient pressure head height under the conditions of appropriate pouring area, pouring temperature and pouring method.
2. Negative pressure;
1) Common negative pressure gauges are installed on the main pipeline, which can only indirectly determine the negative pressure in the box, but cannot represent the actual negative pressure value in the box.
2) Due to differences in casting structure, some castings have narrow passages in the inner cavity. During the pouring process, due to pressure relief or insufficient negative pressure, the negative pressure in this part will be low, resulting in insufficient sand mold strength, deformation and rupture of the casting, and defects such as iron-wrapped sand, box expansion, and box collapse. These areas are negative pressure blind areas.
3) During the pouring, due to improper operation, the plastic film sealing the box surface is burned over a large area, and a large amount of pressure relief is generated due to poor sealing, resulting in serious lack of negative pressure in the box, and even back-spraying during pouring, resulting in cold shut, insufficient pouring and carbon defects in the casting. One box has multiple sieves, and one bag has multiple boxes for pouring, which is extremely obvious.
Specific measures:
A. Install a temporary negative pressure pipe; pre-fill resin sand; replace the sand core.
B. The thickness of the sand cover is sufficient; pre-treatment is performed around the pouring cup, such as asbestos cloth, resin sand, etc.; the negative pressure of the sand box poured previously is reduced or closed; the second standby vacuum pump is turned on.
3.Prevent impurities;
During the pouring process, impurities such as slag, sand particles, ash powder, etc. outside the cavity are immersed in the cavity with the molten iron flow, and defects such as sand holes and slag holes will appear in the casting.
1) The refractoriness, strength and density of the refractory material of the molten iron ladle are not high. During the pouring process, it is corroded and melted with the high-temperature molten iron, and the slag is formed and floats up; loose granular aggregates fall or are washed by the molten iron.
2) The slag hanging on the old ladle is not cleaned up; the density and refractoriness of the material for the lining repair are not high, and the bonding with the original lining is not strong.
3) The slag remover and slag aggregation agent are ineffective, and there are scattered and separated impurities on the surface of the molten iron.
4) When pouring the duckbill ladle, the slag cotton is suspended in the air and loses its slag function.
5) Misalignment during pouring, molten iron impacts the sand surface, and sand splashes into the pouring cup.
6) Impurities such as dust, sand, and dirt exist in the inoculant.
Specific measures:
A. Pack with high-temperature resistant castables and use special repair materials for local repair.
B. Use effective slag removal and slag aggregation agent.
C. The pouring cup is more than 50mm above the sand surface, and the adjacent pouring cups to be poured are covered with protective covers. For unskilled pourers, asbestos cloth is used around the pouring cup to protect it.
D. Educate and train operators on skills and literacy.
E. Place a filter, give priority to bottom pouring, and the pouring system has a slag closing function.
F. The inoculant is purchased at a designated location and properly stored.
4. Pouring temperature;
According to the characteristics of the molten metal and the structural characteristics of the casting, the minimum pouring temperature is determined to ensure that the casting structure is complete, the edges and corners are clear, and there is no cold shut defect in the thin wall.
When a bag of molten iron is poured into multiple boxes and multiple pieces in one box, the influence of the cooling of the molten iron in the later stage is extremely important.
1) Use an insulation bag, generally add an insulation layer between the steel shell and the refractory layer;
2) Cover the surface of the molten iron bag with insulation agent, slag and insulation composite covering agent;
3) The upper limit of the pouring temperature can be appropriately increased without affecting the material, the refractoriness of the mold coating layer is satisfied, and no other casting defects are produced. For example, the motor housing: the furnace temperature is 1630-1650℃, and the pouring temperature is 1470-1580℃;
4) When a small amount of molten iron is left at the end and the temperature is low, it should be returned to the furnace for treatment, or continue to tap and pour;
5) Multiple pieces are poured in series;
6) Change to multiple tapping of small bags;
7) Shorten the time of the pouring process, the pouring cup is arranged consistently, and the pouring worker and the crane worker are skilled and have the best cooperation.
5. Pouring environment.
In the casting production process, there is a saying that "30% modeling and 70% pouring", which shows the importance of pouring in casting production.
The operating skills of the pouring worker are very critical, but it is impossible for everyone to become an "oil seller". Creating a good pouring environment is generally easy to do.
1) The vertical height of the ladle mouth from the upper plane of the pouring cup is ≤300mm, and the horizontal distance between the ladle mouth and the center line of the pouring cup is ≤300mm;
2) Use a duckbill ladle, and the ladle mouth should not be too long. [Reduce the initial velocity of the molten iron leaving the ladle mouth parabola and shorten the horizontal distance;
3) When designing the process and packing, the pouring cup should be placed as close to the casting side of the sand box as possible, with a maximum of two rows;
4) Box-type pouring cup or additional funnel backflow cup;
5) Automatic pouring machine. The ladle is close to the sand box, and the ladle mouth is close to the pouring cup in both horizontal and vertical directions, so it is easy to find the correct position. The trolley and lifting adjustment of the overhead crane are used in the middle, and the ladle is relatively stable, and it is not easy to break the flow or the phenomenon of large and small;
6)The teapot ladle cannot be close to the sand box; the pouring worker is far away and it is not easy to find the correct position. The sand box is placed in multiple rows. When pouring the middle mold, the ladle mouth is too high from the pouring cup, and the horizontal distance is far, which is difficult to control.
二、Ductile iron valve body process design and analysis
1. Structural features and characteristics of castings;
1) Characteristics: valve body, material QT450-10, unit weight 50Kg, outline size 320×650×60mm;
2) Structural features: thick wall 60mm, thin wall 10mm, inner cavity is a circular airway;
3)Special requirements: no air leakage defects on the wall around the airway, no defects such as sand holes, pores, shrinkage, etc. on other processed surfaces.
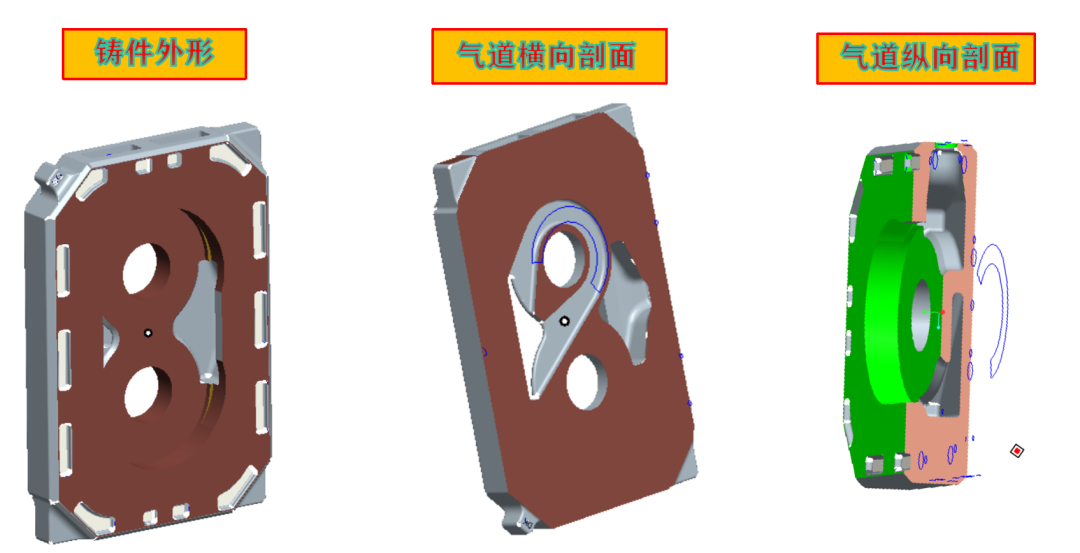
2.Comparison and analysis of two gating system design schemes;
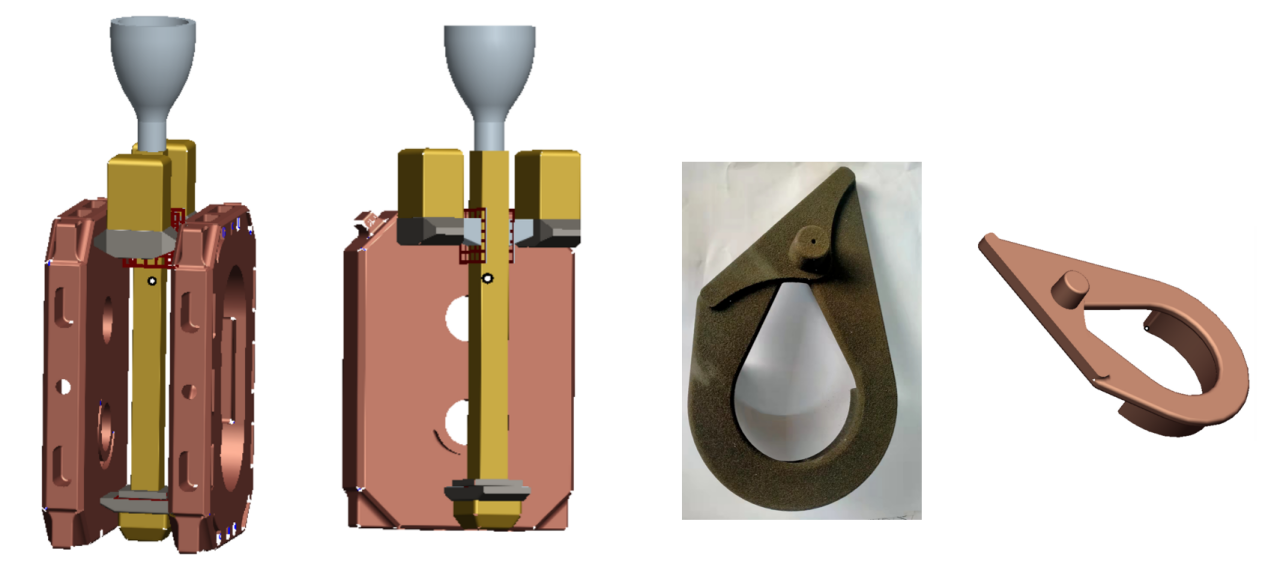
Plan 1,
1) Place vertically, two pieces in one mold, two layers of side injection, the bottom is mainly filled, and the upper part is mainly shrinkage-compensated;
2) The airway is a coated sand core, coated with lost foam water-based paint, and the coating thickness is 1mm;
3) The riser neck is short, flat and thin, with a size of 12 thick × 50 wide. Position: away from the hot spot but close to the hot spot;
4) Riser size: 70×80×150mm high;
5)Casting temperature: 1470~1510℃.
Scheme 2,
1) Place vertically, two pieces in one casting, two layers of side casting, the bottom is mainly filled, and the upper part is mainly shrinkage-compensated;
2) The airway is a coated sand core, and the lost foam water-based coating is applied on the outside, with a coating thickness of 1mm;
3) The riser neck is thick and large, with dimensions: thickness 15×width 50. Position: placed at the upper geometric hot node;
4) Riser size: 80×80×height 160;
5) Pouring temperature: 1470~1510℃.
3. Test results;
Scheme 1, internal and external scrap rate 80%;
There are 10% shrinkage holes around the root of the riser neck of some castings;
After finishing the castings, most castings have shrinkage holes and shrinkage defects in the lower part.
Scheme 2, internal and external scrap rate 20%;
Some castings have 10% shrinkage holes around the root of the riser neck;
After the casting is processed, there are no shrinkage holes and shrinkage defects, but there is a small amount of slag inclusions.
4.Simulation analysis;
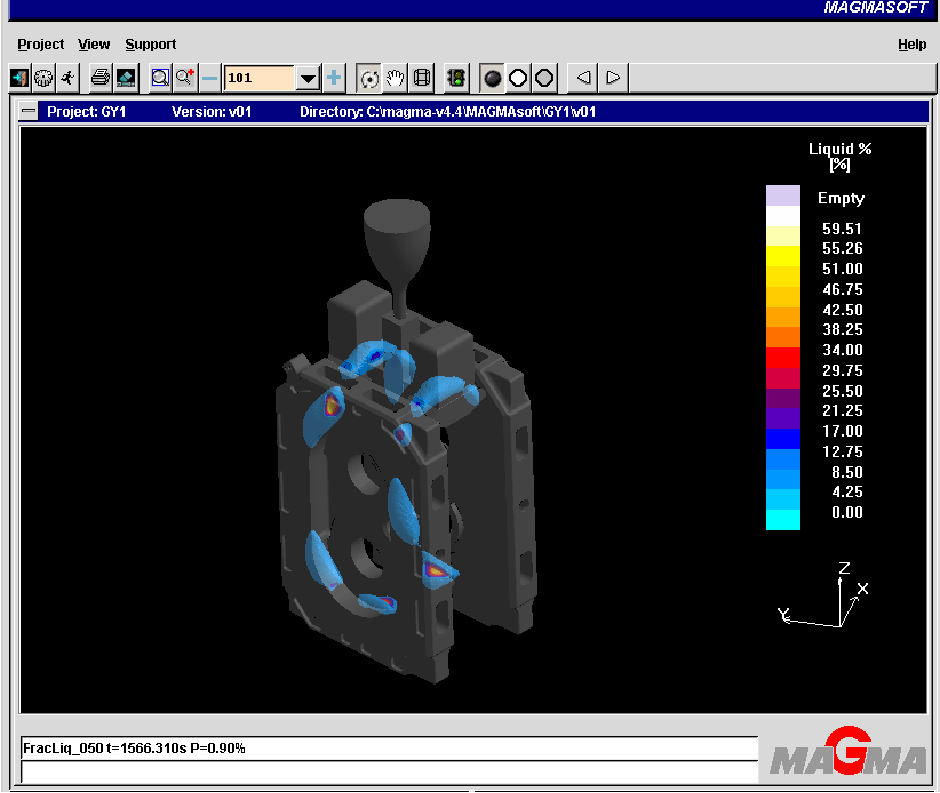
In option 1, there is a risk of shrinkage at the root and lower part of the riser neck; the simulation results are consistent with the actual defects of the casting.
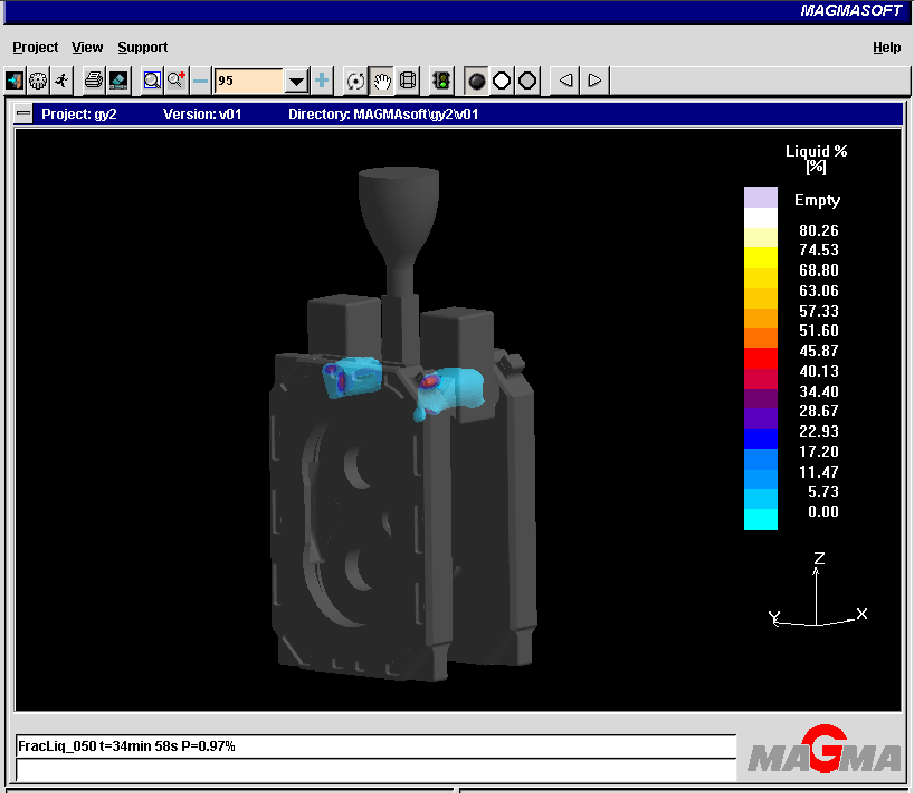
In the second scheme, there is a risk of shrinkage at the root of the riser neck, and the simulation results are consistent with the actual defects of the casting.
5. Process improvement and process analysis.
1) Process improvement:
There is a shrinkage at the root of the riser, indicating that the heat capacity of the riser is relatively small. On the basis of scheme 2, the riser and the riser neck are appropriately enlarged.
Original size: riser 80×80×height 160 riser neck 15×50;
After improvement: riser 80×90×height 170 riser neck 20×60;
Verification results: shrinkage and shrinkage defects are eliminated, and the internal and external scrap rates are ≤5%.
2) Process analysis:
Place the two large planes on the side, and cast the two pieces in series. The vertical projection area is the smallest, and the large plane is on the facade, which is conducive to reducing the instantaneous gas emission; and most of the important processing surfaces are on the side.
Two-layer side casting, open casting system. The upper cross runner is tilted upward, and the lower ingrate area is larger than the straight runner, so that the molten iron is injected from the bottom first, which is conducive to the smooth rise of the molten iron. The foam vaporizes layer by layer, and the ingrate is quickly closed. Air and slag cannot enter the cavity, avoiding carbon defects and slag inclusions.
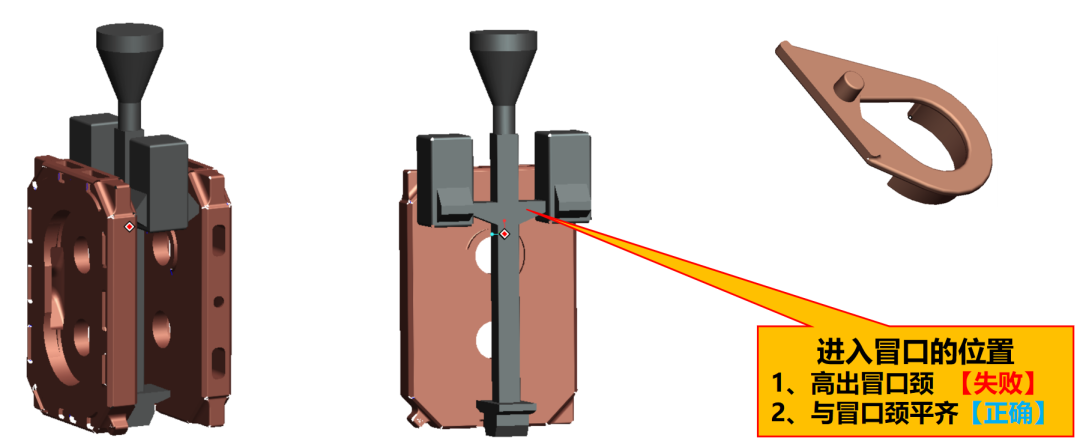
When the molten iron rises to the height of the root of the upper riser, most of the high-temperature molten iron first enters the cavity through the riser. The riser is overheated and approximates a hot riser, not a completely hot riser, because the cavity needs to rise a small amount of cold molten iron through the bottom ingrate, so the volume of the riser is larger than that of the hot riser, so that it solidifies last.
The runner connecting the upper straight runner to the riser must be flush with the riser neck. If it is higher, the lower part of the riser is all cold molten iron, the riser shrinkage compensation efficiency is seriously reduced, and cold shut and carbon defects will appear on the upper part of the casting, which has been proven in practice.
With a closed pouring system, the molten iron rises to a certain height, and the molten iron enters the cavity from the upper and lower water inlets at the same time. At this time, the riser becomes a hot riser, and the height of the cross runner connecting the riser has little effect.
The open pouring system has no slag function, and a filter must be set at the upper and lower water inlets.
The airway core is surrounded by molten iron and the environment is harsh. Therefore, the core must have high strength, refractoriness, and disintegration. A coated sand core is used, and the surface is coated with lost foam coating. The coating thickness is 1 to 1.5 mm.
P.S. Discussion on shrinkage feed risers,
1) The riser neck is at the actual hot node position, the thickness and area cannot be too small [the modulus cannot be too small], and the inner runner connecting the riser is flat, thin and long. The riser is large.
2) The riser neck is away from the actual hot node position, but close to the hot node, flat, thin and short. The riser is small.
The wall thickness of the casting is large, so 1 is selected); the wall thickness of the casting is small, so 2 is selected).
Scheme 3 [Not tested]
1) Injection from the top, molten iron enters the cavity through the riser, a true hot riser;
2) The runners of the sprue and the riser are higher than the riser neck;
3) Advantages: easy to compensate for shrinkage and easy to fill the mold;
4)Disadvantages: Unstable molten iron filling, easy to produce carbon defects.
三、 Six issues that casting technicians should pay attention to
1) Fully understand the structural characteristics, technical requirements and special features of the product,
[Minimum wall thickness, airway, safety, high pressure, leakage, use environment]
2) Investigate the problems that are currently prone to occur in the casting and use process of this product or similar products,
[Many seem simple, but hide crises]
3) Select the best casting method,
[The lost foam process has many safety parts, leakage, high pressure, etc., which are not the best solution]
4) For new products supplied in batches, it is necessary to invite an experienced expert group to demonstrate, review and guide,
[People start to need help when they are born]
5) When the casting structure types are complex, changeable, and the quantity is small, early casting simulation is very necessary,
[Reduce the number of tests and be targeted]
6)Let me ask: A technician has the same products and processes in different companies, but why is the quality so different?
四、 Typical Cases
1) For the automobile ductile iron wheel reducer shell, the best casting method is to cover the iron mold with sand. The process yield is 85%, and the comprehensive scrap rate is ≤5%. The quality is stable and the production efficiency is high; the lost foam process is a failure.
[It was feasible to conduct casting simulation in the United States. Due to the determination of the casting structure and technical requirements, in addition to the riser shrinkage compensation and local cold iron measures, the overall casting cooling speed is very critical. ]
2) For various ductile iron brackets of automobiles, the lost foam process is not advisable. Any casting defects inside the casting can cause fractures during use. If 1% of the internal carbon defects occur, claims and fines will be made afterwards, which will make you lose all your previous efforts and go bankrupt. The number of small parts is large, and 100% flaw detection cannot be done.
For the automobile balance shaft bracket, the material is QT800-5, and the lost foam process is not advisable. Even if the casting has no defects, the graphite is coarse due to the slow cooling speed of the casting, and the subsequent heat treatment is powerless.
3) The size of the aluminum can is 30mm in wall thickness, 500mm in outer diameter, and 1000mm in height. Nuclear waste container, no defects inside the casting. Japan once asked China, known as a casting power, to make it at a price 10 times higher than the market price. After the national casting authority group reviewed it, the conclusion was "can't do it".
[The entire smelting and pouring must be in a vacuum environment to ensure quality]
4) A large domestic lost foam casting company spent a lot of money on lost foam production of ductile iron parts. It asked the national casting authority group for guidance, but failed. Now it has changed to clay sand and static pressure line production.
5) Fastening nuts are very simple and require never loosening. In the past, only Japan could manufacture them in the world. Some seem simple, but they are actually very complicated.
6) For gray cast iron, motor housing, bed, workbench, gearbox housing, clutch housing and other box parts, the lost foam process is the best process.
7) Lost foam is first burned and then poured, as well as empty shell molding, which brings light to the production of stainless steel and duplex steel castings with special requirements for safety parts, leakage, high pressure resistance, etc.
Post time: Jul-08-2024





