The chemical composition of ceramic sand is mainly Al2O3 and SiO2, and the mineral phase of ceramic sand is mainly corundum phase and mullite phase, as well as a small amount of amorphous phase. The refractoriness of ceramic sand is generally greater than 1800°C, and it is a high-hardness aluminum-silicon refractory material.
Characteristics of ceramic sand
● High refractoriness;
● Small coefficient of thermal expansion;
● High thermal conductivity;
● Approximate spherical shape, small angle factor, good fluidity and compact ability;
● Smooth surface, no cracks, no bumps;
● Neutral material, suitable for various casting metal materials;
● The particles have high strength and are not easily broken;
● The particle size range is wide, and the mixing can be customized according to the process requirements.
Application of Ceramic Sand in Engine Castings
1. Use ceramic sand to solve the veining, sand sticking, broken core and sand core deformation of cast iron cylinder head
● Cylinder block and cylinder head are the most important castings of the engine
● The shape of the inner cavity is complex, and the requirements for dimensional accuracy and inner cavity cleanliness are high
● Large batch
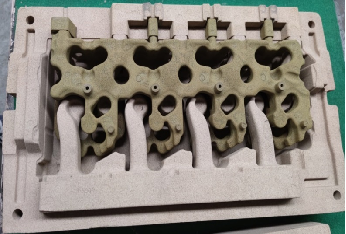
In order to ensure production efficiency and product quality,
● Green sand (mainly Hydrostatic styling line) assembly line production is generally used.
● Sand cores generally use cold box and resin coated sand (shell core) process, and some sand cores use hot box process.
● Due to the complex shape of the sand core of the cylinder block and head casting, some sand cores have a small cross-sectional area, the thinnest part of some cylinder blocks and cylinder head water jacket cores is only 3-3.5mm, and the sand outlet is narrow, the sand core after casting surrounded by high-temperature molten iron for a long time, it is difficult to cleaning sand, and special cleaning equipment is needed, etc. In the past, all silica sand was used in casting production, which caused veins and sand sticking problems in the water jacket castings of cylinder block and cylinder head. Core deformation and broken core problems are very common and difficult to solve.
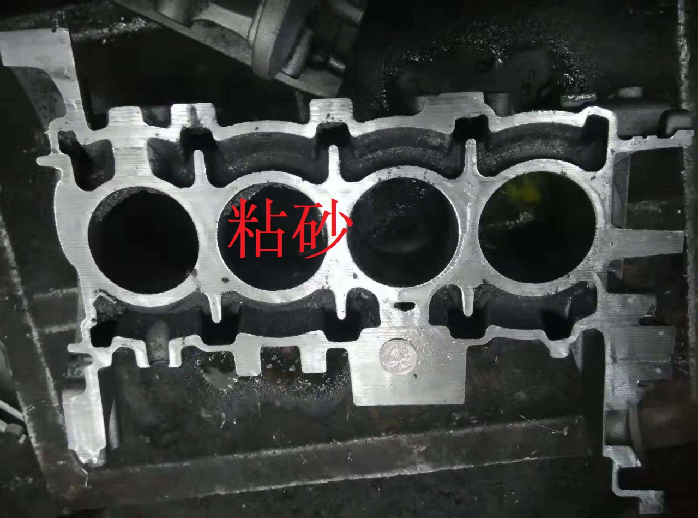

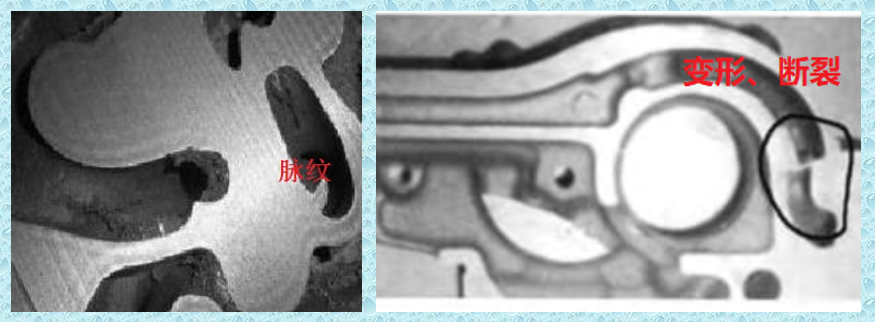
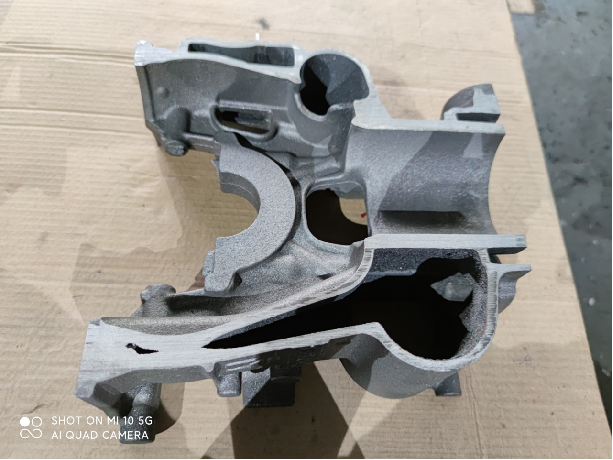

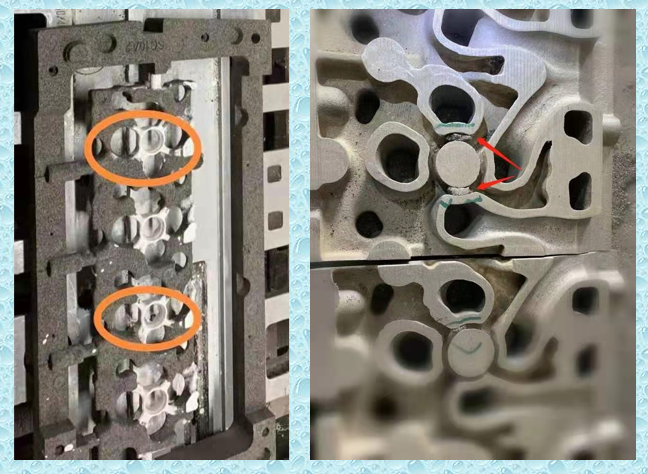

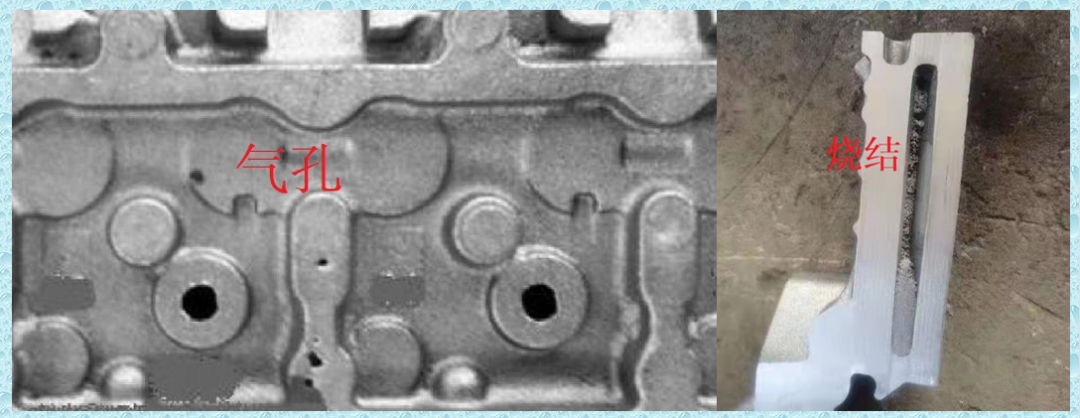
In order to solve such problems, starting from around 2010, some well-known domestic engine casting companies, such as FAW, Weichai, Shangchai, Shanxi Xinke, etc., began to research and test the application of ceramic sand to produce cylinder blocks, cylinder head water jackets, and oil passages. Equal sand cores effectively eliminate or reduce defects such as inner cavity sintering, sand sticking, sand core deformation, and broken cores.
Follow pictures are made by ceramic sand with cold box process.
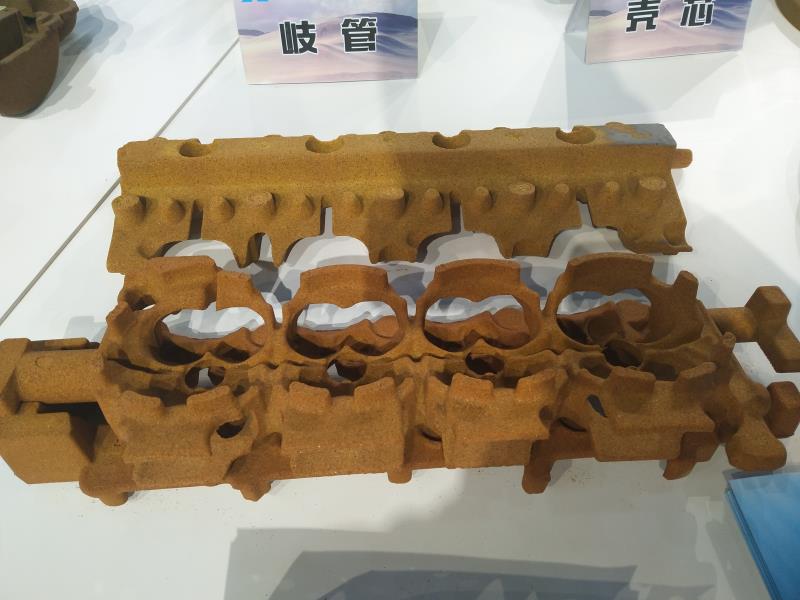
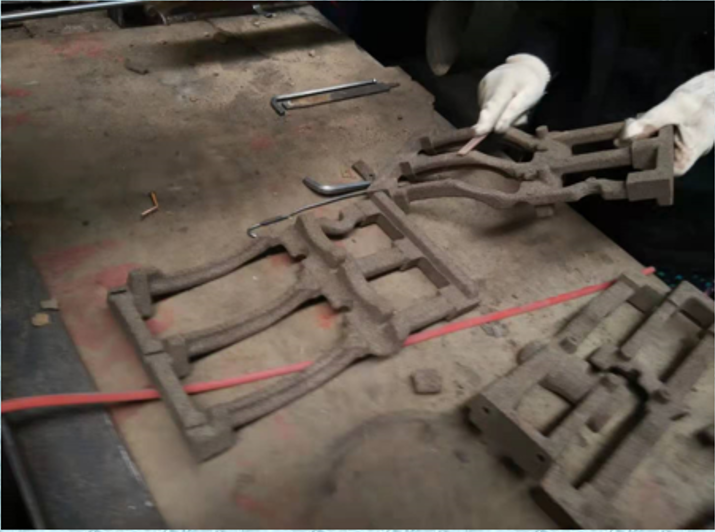
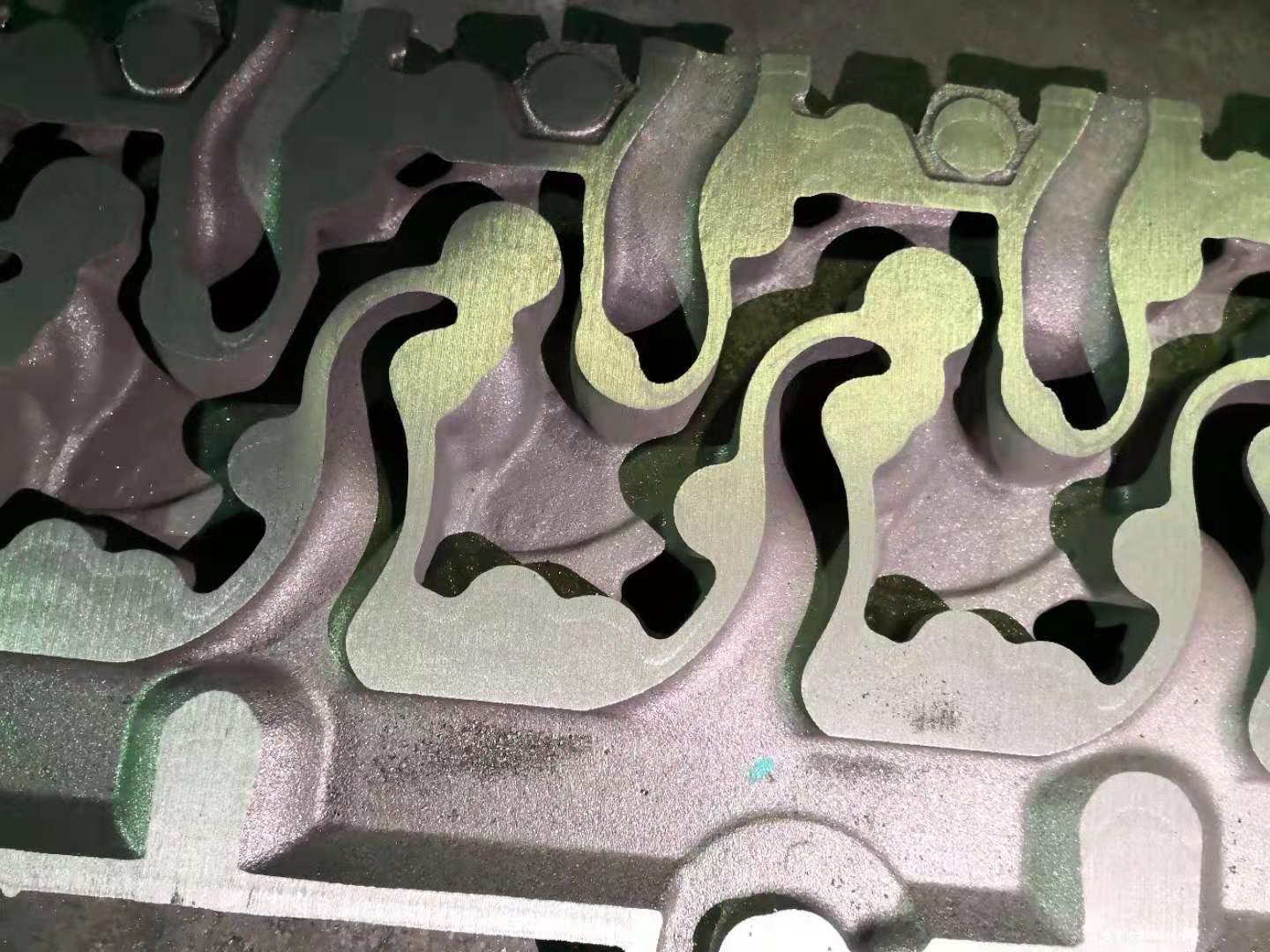




Since then, ceramic sand mixed scrubbing sand has been gradually promoted in cold box and hot box processes, and applied to cylinder head water jacket cores. It has been in stable production for more than 6 years. The current usage of the cold box sand core is: according to the shape and size of the sand core, the amount of ceramic sand added is 30%-50%, the total amount of resin added is 1.2%-1.8%, and the tensile strength is 2.2-2.7 MPa. (Laboratory sample testing data)
Summary
Cylinder block and head cast iron parts contain many narrow inner cavity structures, and the pouring temperature is generally between 1440-1500°C. The thin-walled part of the sand core is easily sintered under the action of high-temperature molten iron, such as molten iron infiltrating into the sand core,or produce interface reaction to form sticky sand. The refractoriness of ceramic sand is greater than 1800°C, meanwhile, the true density of ceramic sand is relatively high, the kinetic energy of sand particles with the same diameter and speed is 1.28 times that of silica sand particles when shooting sand, which can increase the density of sand cores.
These advantages are the reasons why the use of ceramic sand can solve the problem of sand sticking in the inner cavity of cylinder head castings.
The water jacket, intake and exhaust parts of the cylinder block and cylinder head often have veining defects. A large number of researches and casting practices have shown that the root cause of the veining defects on the casting surface is the phase change expansion of silica sand, which causes thermal stress leads to cracks on the surface of the sand core, which causes molten iron to penetrate into the cracks, the tendency of veins is greater especially in the cold box process. In fact, the thermal expansion rate of silica sand is as high as 1.5%, while the thermal expansion rate of ceramic sand is only 0.13% (heated at 1000°C for 10 minutes). The possibility of cracking is very small where on the surface of the sand core due to thermal expansion stress. The use of ceramic sand in the sand core of the cylinder block and cylinder head is currently a simple and effective solution to the problem of veining.
Complicated, thin-walled, long and narrow cylinder head water jacket sand cores and cylinder oil channel sand cores require high strength (including high temperature strength) and toughness, and at the same time need to control the gas generation of the core sand. Traditionally, the coated sand process is mostly used . The use of ceramic sand reduces the amount of resin and achieves the effect of high strength and low gas generation. Due to the continuous improvement of the performance of resin and raw sand, the cold box process has increasingly replaced part of the coated sand process in recent years, greatly improving production efficiency and improving the production environment.
2. Application of ceramic sand to solve the problem of sand core deformation of exhaust pipe
Exhaust manifolds work under high-temperature alternating conditions for a long time, and the oxidation resistance of materials at high temperatures directly affects the service life of exhaust manifolds. In recent years, the country has continuously improved the emission standards of automobile exhaust, and the application of catalytic technology and turbocharging technology has significantly increased the working temperature of the exhaust manifold, reaching above 750 °C. With the further improvement of engine performance, the working temperature of the exhaust manifold will also increase. At present, heat-resistant cast steel is generally used, such as ZG 40Cr22Ni10Si2 (JB/T 13044), etc., with a heat-resistant temperature of 950°C-1100°C.
The inner cavity of the exhaust manifold is generally required to be free from cracks, cold shuts, shrinkage cavities, slag inclusions, etc. that affect the performance, and the roughness of the inner cavity is required to be no greater than Ra25. At the same time, there are strict and clear regulations on the deviation of the pipe wall thickness. For a long time, the problem of uneven wall thickness and excessive deviation of the exhaust manifold pipe wall has plagued many exhaust manifold foundries.


A foundry first used silica sand coated sand cores to produce heat-resistant steel exhaust manifolds. Due to the high pouring temperature (1470-1550°C), the sand cores were easily deformed, resulting in out-of-tolerance phenomena in pipe wall thickness. Although the silica sand has been treated with high-temperature phase change, due to the influence of various factors, it still cannot overcome the deformation of the sand core at high temperature, resulting in a wide range of fluctuations in the thickness of the pipe wall, and in severe cases, it will be scrapped. In order to improve the strength of the sand core and control the gas generation of the sand core, it was decided to use ceramic sand coated sand. When the amount of resin added was 36% lower than that of silica sand coated sand, its room temperature bending strength and thermal bending strength increased by 51% , 67%, and the amount of gas generation is reduced by 20%, which meets the process requirements of high strength and low gas generation.
The factory uses silica sand-coated sand cores and ceramic sand-coated sand cores for simultaneous casting, after cleaning the castings, they conduct anatomical inspections.
If the core is made of silica sand coated sand, the castings have uneven wall thickness and thin wall, and the wall thickness is 3.0-6.2 mm; when the core is made of ceramic sand coated sand, the wall thickness of the casting is uniform, and the wall thickness is 4.4-4.6 mm. as follow picture

Silica sand coated sand

Ceramic sand coated sand
Ceramic sand coated sand is used to make cores, which eliminates sand core breakage, reduces sand core deformation, greatly improves the dimensional accuracy of the inner cavity flow channel of the exhaust manifold, and reduces sand sticking in the inner cavity, improving the quality of castings and finished products rate and achieved significant economic benefits.
3. Application of ceramic sand in turbocharger housing
The working temperature at the turbine end of the turbocharger shell generally exceeds 600°C, and some even reach as high as 950-1050°C. The shell material needs to be resistant to high temperatures and has good casting performance. The shell structure is more compact, the wall thickness is thin and uniform, and the inner cavity is clean, etc. , is extremely demanding. At present, the turbocharger housing is generally made of heat-resistant steel casting (such as 1.4837 and 1.4849 of the German standard DIN EN 10295), and heat-resistant ductile iron is also used (such as the German standard GGG SiMo, the American standard high-nickel austenitic nodular iron D5S, etc.).
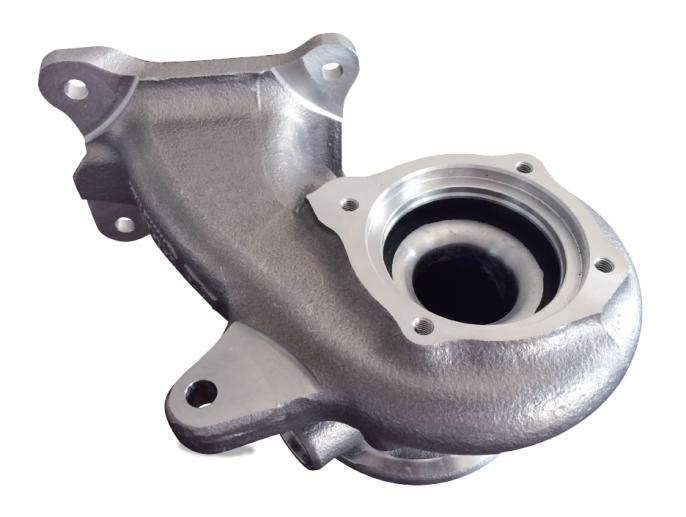
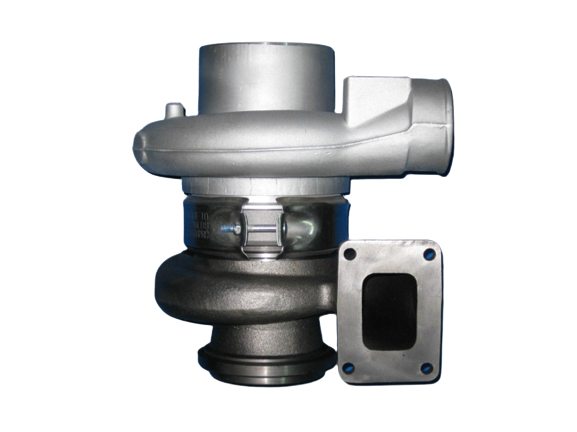


A 1.8 T engine turbocharger housing, material: 1.4837, namely GX40CrNiSi 25-12, main chemical composition (%): C: 0.3-0.5, Si: 1-2.5, Cr: 24-27, Mo: Max 0.5, Ni: 11-14, pouring temperature 1560 ℃. The alloy has a high melting point, a large shrinkage rate, a strong hot cracking tendency, and high casting difficulty. The metallographic structure of the casting has strict requirements on residual carbides and non-metallic inclusions, and there are also specific regulations on casting defects. In order to ensure the quality and production efficiency of castings, the molding process adopts core casting with film-coated sand shell cores (and some cold box and hot box cores). Initially, AFS50 scrubbing sand was used, and then roasted silica sand was used, but problems such as sand sticking, burrs, thermal cracks, and pores in the inner cavity appeared to varying degrees.
On the basis of research and testing, the factory decided to use ceramic sand. Initially purchased finished coated sand (100% ceramic sand), and then purchased regeneration and coating equipment, and continuously optimized the process during the production process, use ceramic sand and scrubbing sand to mix raw sand. At present, the coated sand is roughly implemented according to the follow table:
|
Ceramic sand-coated sand process for turbocharger housing |
||||
| Sand Size | Rate of ceramic sand % | Resin addition % | Bending strength MPa | Gas output ml/g |
| AFS50 | 30-50 | 1.6-1.9 | 6.5-8 | ≤12 |

Over the past few years, the production process of this plant has been running stably, the quality of castings is good, and the economic and environmental benefits are remarkable. The summary is as follows:
a. Using ceramic sand, or using a mixture of ceramic sand and silica sand to make cores, eliminates defects such as sand sticking, sintering, veining, and thermal cracking of castings, and realizes stable and efficient production;
b. Core casting, high production efficiency, low sand-iron ratio (generally no more than 2:1), less raw sand consumption, and lower costs;
c. Core pouring is conducive to the overall recycling and regeneration of waste sand, and the thermal reclamation is adopted uniformly for regeneration. The performance of regenerated sand has reached the level of new sand for scrubbing sand, which has achieved the effect of reducing the purchase cost of raw sand and reducing solid waste discharge;
d. It is necessary to frequently check the content of ceramic sand in regenerated sand to determine the amount of new ceramic sand added;
e. Ceramic sand has round shape, good fluidity, and large specificity. When mixed with silica sand, it is easy to cause segregation. If necessary, the sand shooting process needs to be adjusted;
f. When covering the film, try to use high-quality phenolic resin, and use various additives with caution.
4. Application of ceramic sand in engine aluminum alloy cylinder head
In order to improve the power of automobiles, reduce fuel consumption, reduce exhaust pollution, and protect the environment, lightweight automobiles are the development trend of the automobile industry. At present, automotive engine (including diesel engine) castings, such as cylinder blocks and cylinder heads, are generally cast with aluminum alloys, and the casting process of cylinder blocks and cylinder heads, when using sand cores, metal mold gravity casting and low pressure casting (LPDC) are the most representative.

The sand core, coated sand and cold box process of aluminum alloy cylinder block and head castings are more common, suitable for high-precision and large-scale production characteristics. The method of using ceramic sand is similar to the production of cast iron cylinder head. Due to the low pouring temperature and small specific gravity of aluminum alloy, generally low-strength core sand is used, such as a cold box sand core in a factory, the amount of resin added is 0.5-0.6%, and the tensile strength is 0.8-1.2 MPa. Core sand is required Has good collapsibility. The use of ceramic sand reduces the amount of resin added and greatly improves the collapse of the sand core.
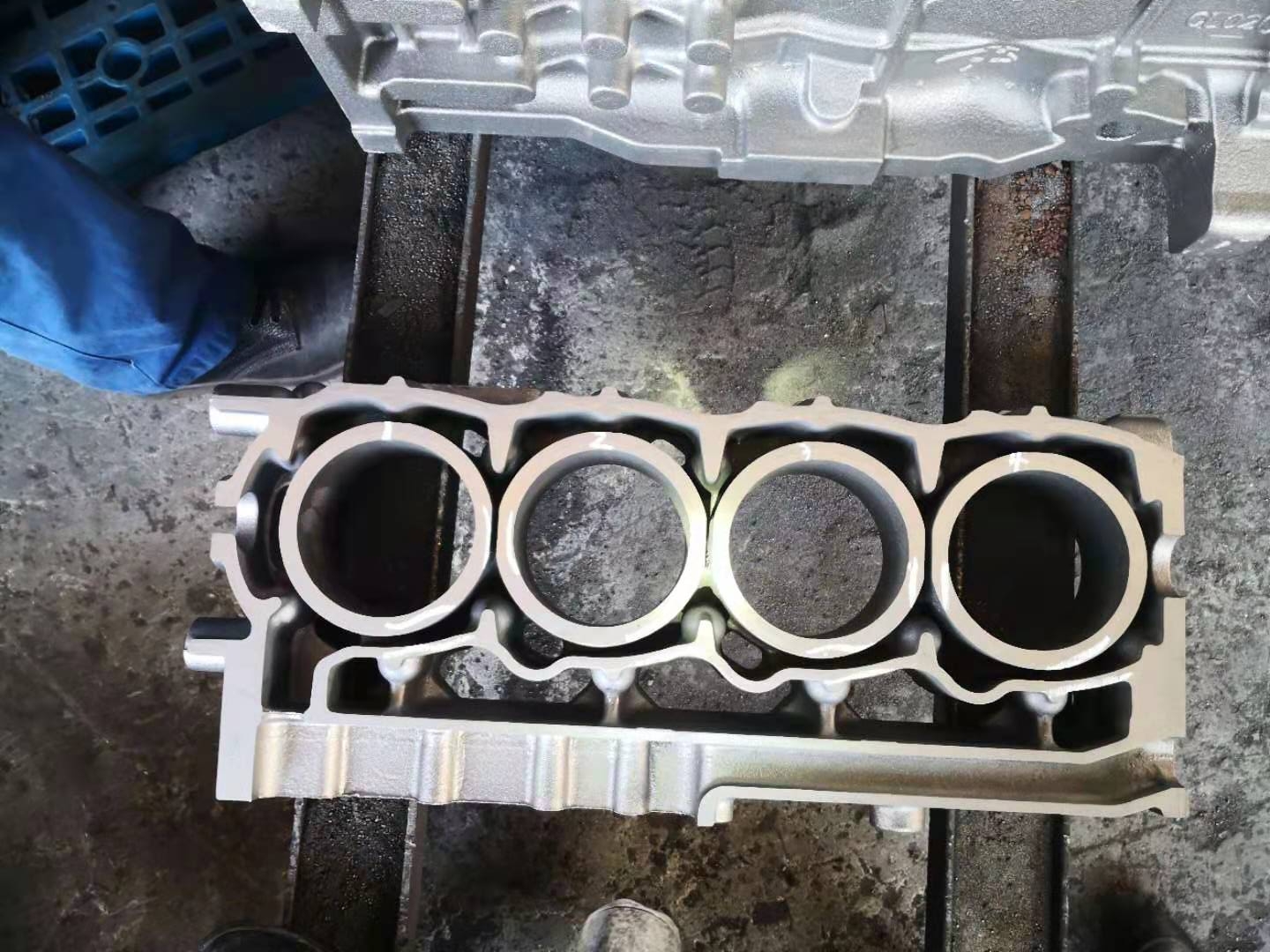
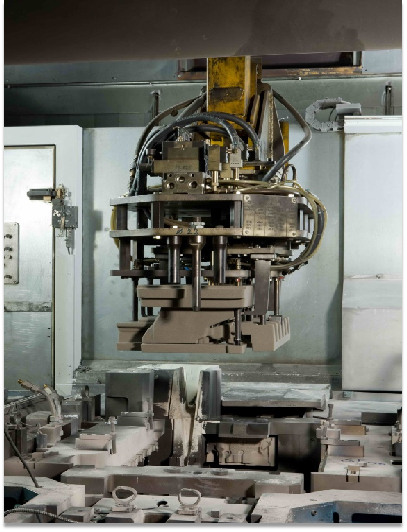
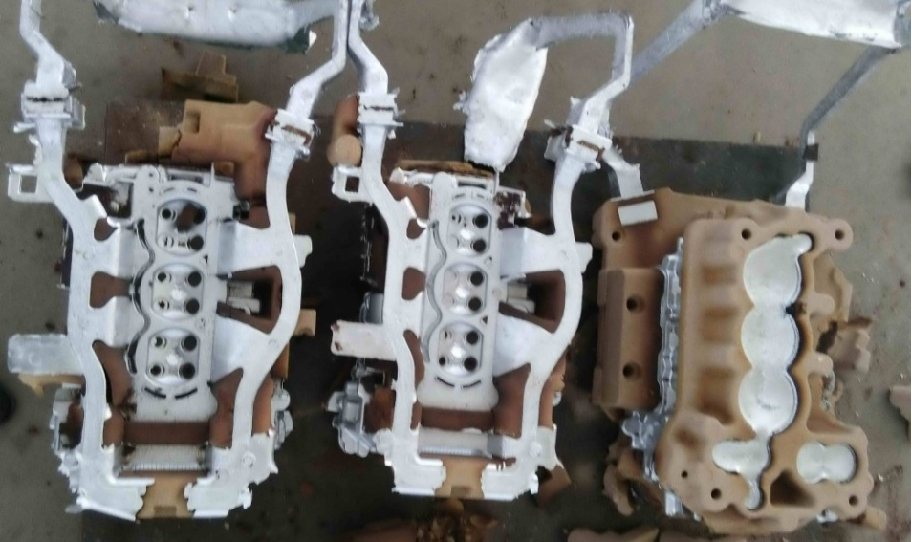
In recent years, in order to improve the production environment and improve the quality of castings, there are more and more researches and applications of inorganic binders (including modified water glass, phosphate binders, etc.). The picture below is the casting site of a factory using ceramic sand inorganic binder core sand aluminum alloy cylinder head.


The factory uses ceramic sand inorganic binder to make the core, and the amount of binder added is 1.8~2.2%. Due to the good fluidity of ceramic sand, the sand core is dense, the surface is complete and smooth, and at the same time, the amount of gas generation is small, it greatly improves the yield of castings, improves the collapsibility of core sand, improves the production environment, and becomes a model of green production.


The application of ceramic sand in the engine casting industry has improved production efficiency, improved the working environment, solved casting defects, and achieved significant economic benefits and good environmental benefits.
The engine foundry industry should continue to increase the regeneration of core sand, further improve the use efficiency of ceramic sand, and reduce solid waste emissions.
From the perspective of the use effect and scope of use, ceramic sand is currently the casting special sand with the best comprehensive performance and the largest consumption in the engine casting industry.
Post time: Mar-27-2023





